Monkeys share many traits with people — together with our thirst for alcohol.
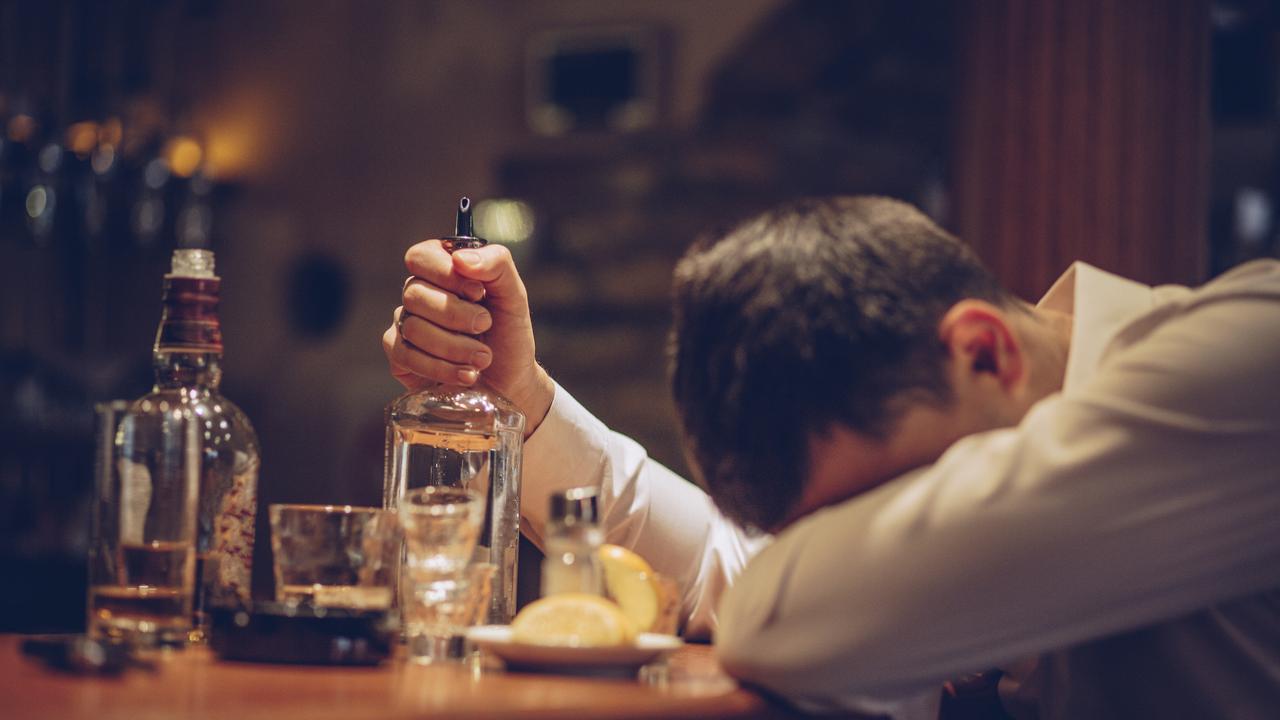
US medical researchers had been in a position to flip eight rhesus macaque monkeys into heavy drinkers by providing them growing concentrations of alcohol, the New York Post stories.
With free entry to booze all day over a interval of six months, it wasn’t lengthy earlier than the monkeys had been true occasion animals, binge ingesting regularly.
The goal of the analysis was to check a kind of gene remedy — at the moment used to deal with Parkinson’s illness — within the hope that it’d sometime assist individuals with extreme alcoholism.
“We know that we can get people with alcohol use disorder to stop drinking for short periods of time” with medicine, Dr Kathleen Grant, a neuroscientist at Oregon Health & Science University, informed Wired.
“But the desire to drink again often supersedes taking their medications.”
Dr Grant and a crew from a number of different analysis centres injected a gene remedy into the brains of 4 of the eight alcoholic monkeys.
The injections contained a progress issue protein known as glial cell line-derived necrotrophic issue, or GDNF.
Earlier research have proven that GDNF can stimulate the manufacturing of dopamine, a neurotransmitter within the mind that performs a task in rewarding addictive behaviour.
So, Dr Grant and her colleagues used magnetic resonance imaging to information the injection of GDNF into the ventral tegmental space of the mind, the place neurons are situated that make dopamine and distribute it all through the mind.
“This was incredibly effective,” Dr Grant mentioned in a news launch. “Drinking went down to almost zero.
“For months on end, these animals would choose to drink water and just avoid drinking alcohol altogether,” she added.
“They decreased their drinking to the point that it was so low we didn’t record a blood-alcohol level.”
Moreover, the GDNF therapy has long-lasting advantages. After a yr, alcohol use among the many 4 handled monkeys dropped by greater than 90 per cent, in comparison with the management group of monkeys that didn’t obtain the therapy.
“It was as if they were learning that the alcohol just wasn’t something they wanted to engage in anymore,” Dr Grant mentioned.
Dopamine performs a important position in alcoholism. “Dopamine is involved in reinforcement of behaviour, and in people finding certain things pleasurable,” Dr Grant mentioned.
“Acute alcohol use can increase dopamine. However, by drinking it chronically, the brain adapts in such a way that it decreases the release of dopamine,” she added.
“So when people are addicted to alcohol, they don’t really feel more pleasure in drinking. It seems that they’re drinking more because they feel a need to maintain an intoxicated state.”
The process isn’t but prepared for human trials, and even when it had been utilized in people, this sort of mind surgical procedure would solely be utilized in probably the most extreme instances of alcoholism.
That’s partly as a result of the therapy is irreversible and completely alters the mind, elevating medical in addition to moral points.
“It would be most appropriate for people who have already shown that all our normal therapeutic approaches do not work for them,” Dr Grant mentioned.
“They are likely to create severe harm or kill themselves or others due to their drinking.
“This would be a last resort if all other treatment options fail.”
This article initially appeared on the New York Post and was reproduced with permission
Originally revealed as Injecting ‘incredibly effective’ gene into the mind may treatment alcoholism: examine
Source: www.dailytelegraph.com.au